When you focus on Choosing the Right Anti Adhesion Gel for Your Hospital or Clinic, you should look for products that offer safety, biodegradability, and easy application. You also want a gel that matches the healing timeline of your patients. The use of these gels is growing worldwide because they help reduce complications after surgery.
|
Region |
CAGR (%) |
Period |
Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
|
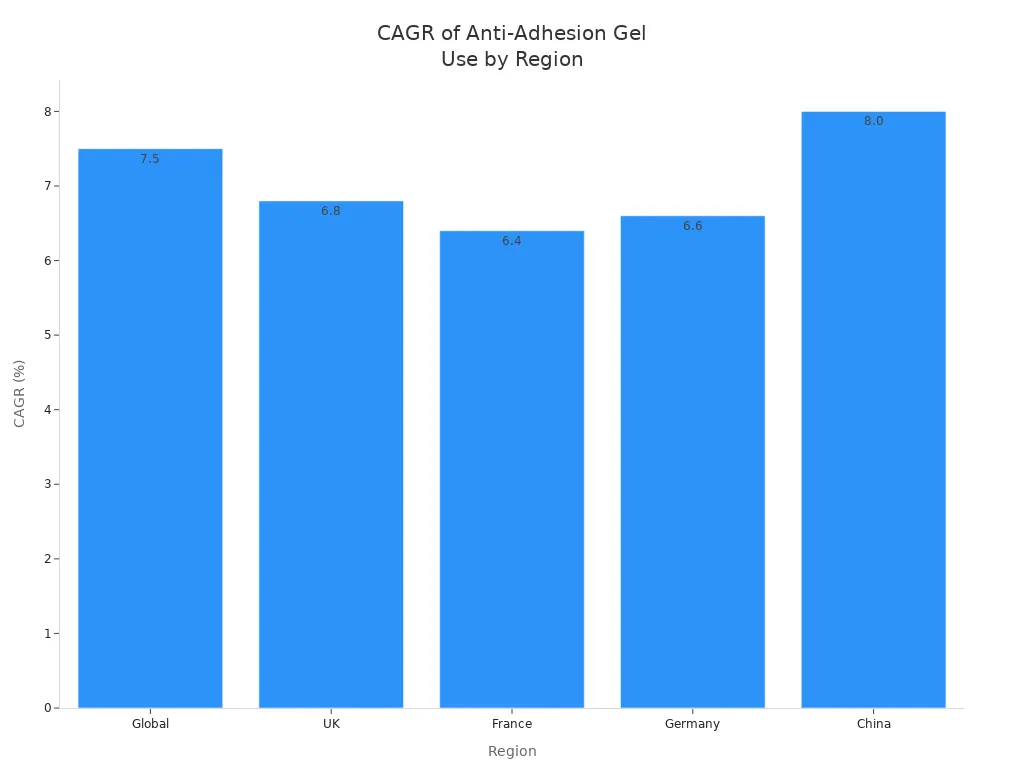
Global |
7.5 |
2025-2035 |
Awareness of postoperative adhesion complications |
|
UK |
6.8 |
2025-2035 |
Demand for minimally invasive interventions |
|
France |
6.4 |
2025-2035 |
Preventive approaches for complications |
|
Germany |
6.6 |
2025-2035 |
More colorectal, gynecological, orthopedic procedures |
|
China |
8.0 |
2025-2035 |
More surgeries and better healthcare infrastructure |
Key Takeaways
Choose anti-adhesion gels that prioritize safety and biocompatibility. Look for FDA or CE approvals to ensure they are safe for patients.
Select gels with strong clinical evidence showing effectiveness in reducing adhesions and improving patient outcomes. Research studies can guide your choice.
Consider the biodegradability of the gel. It should break down safely in the body without causing complications during the healing process.
Ensure the gel is easy to apply and versatile for various surgical procedures. A user-friendly product can enhance surgical efficiency.
Trust reliable manufacturers with a history of innovation and strong clinical trial data. This ensures you are using high-quality products.
Anti Adhesion Gels Overview
What Are Anti Adhesion Gels
You use anti-adhesion gels to stop tissues from sticking together after surgery. These gels help lower the risk of problems that can happen when organs or tissues join by accident. You often see them in surgeries involving the abdomen and pelvis. Surgeons apply these gels during the operation to create a barrier between tissues.
Anti-adhesion gels are designed to prevent tissues from sticking together after surgery.
They are applied during surgical procedures to reduce the risk of postoperative adhesions.
You will find them commonly used in abdominal and pelvic surgeries.
When you use these gels, you help patients recover with fewer complications and less pain.
How They Work in Surgery
Anti-adhesion gels work in several ways to protect your patients. They act as a shield, stopping tissues from touching each other while healing. Some gels also reduce inflammation, which is a big reason adhesions form. Others change how immune cells behave, making the healing process smoother.
|
Mechanism |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Physical Barrier |
Hydrogels cover the damaged area, stopping tissues from sticking together. |
|
Anti-inflammatory Action |
Some gels lower swelling and inflammation after surgery. |
|
Macrophage Polarization |
Certain gels help immune cells calm down, which reduces harmful inflammation. |
|
Scavenger Receptor Action |
Special ingredients prevent immune cells from gathering and causing adhesions at the surgery site. |
You can see that these gels do more than just sit between tissues-they actively support healing.
Common Materials and Innovations
You will find many types of materials in anti-adhesion gels. Some use natural substances like gelatin, which is gentle on the body and fights inflammation. Others use synthetic materials that last longer but may take more time to break down. Newer gels use smart designs, like thermosensitive hydrogels that turn solid at body temperature, making them easy to use in minimally invasive surgeries.
|
Material Type |
Characteristics |
Innovations |
|---|---|---|
|
Gelatin-based systems |
GPP20 hydrogel with easy, one-step preparation |
|
|
Human amniotic membrane |
Supports healing, but breaks down quickly |
- |
|
Microgel-based cream hydrogels |
Injectable, slow to break down, reduces inflammation |
- |
|
Synthetic hydrogels |
Last longer, but may break down slowly |
- |
|
Janus hydrogel |
Sticks well to wet tissue, easy to prepare |
- |
|
GPP20 hydrogel |
Gels quickly, injectable, self-healing |
Overcomes old material limits with better performance |
Thermosensitive hydrogels can be injected as a liquid and turn into a gel at body temperature.
Nanofibrous films use special fibers to stop adhesions.
Some gels mix polymer meshes with hydrogels for extra strength.
You can see that new materials make these gels safer, easier to use, and more effective for your patients.
Why Anti Adhesion Gels Matter in Hospitals and Clinics
Clinical Benefits and Outcomes
You want your patients to heal well after surgery. Anti-adhesion gels help you reach this goal. These gels lower the risk of tissues sticking together, which can cause pain and problems later. When you use these gels, you see fewer new adhesions and milder cases when they do happen. Surgeons report that patients experience less pain and recover faster.
You can improve patient comfort and reduce complications by choosing the right gel.
Researchers studied how these gels work in hospitals. They found that patients who received anti-adhesion gels had better results. The table below shows some key findings:
|
Outcome |
Result |
Confidence Interval |
P-value |
Studies |
Sample Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
RR 0.65 |
95% CI 0.45 to 0.93 |
0.02 |
5 |
372 |
|
|
Lower mean adhesion score (general) |
MD -1.44 |
95% CI -1.83 to -1.05 |
<0.00001 |
1 |
24 |
|
Lower mean adhesion score (intrauterine) |
MD -3.30 |
95% CI -3.43 to -3.17 |
<0.00001 |
1 |
19 |
|
More stage I (mild) adhesions |
RR 2.81 |
95% CI 1.13 to 7.01 |
0.03 |
4 |
79 |
You see that gels help reduce new adhesions and make existing ones less severe. Patients also have more mild cases, which are easier to treat.
Advances in Biomaterials
You benefit from new biomaterials in anti-adhesion gels. Scientists create gels that match your needs in the operating room. Modern gels use smart materials that respond to body temperature. You can inject these gels as liquids, and they turn into solids inside the body. This makes them easy to use in small spaces.
Some gels use natural ingredients like gelatin or human amniotic membrane. These materials support healing and break down safely. Synthetic gels last longer and give you more control over the healing process. New designs, such as nanofibrous films and polymer meshes, add strength and flexibility.
You can choose gels that fit your procedure and help your patients heal faster.
You see more options every year. These advances let you pick the best gel for each patient and surgery.
Choosing the Right Anti Adhesion Gel for Your Hospital or Clinic
When you focus on Choosing the Right Anti Adhesion Gel for Your Hospital or Clinic, you want to make decisions that protect your patients and support your surgical team. You need to look at several important factors. These include safety, biodegradability, ease of use, and how well the gel matches the healing timeline. You also want to consider the materials used and the reliability of the manufacturer. This section will help you understand each factor so you can make the best choice for your hospital or clinic.
Safety and Biocompatibility
You must always put safety first when Choosing the Right Anti Adhesion Gel for Your Hospital or Clinic. The gel should not cause allergic reactions or trigger the immune system. It should be free from toxins and safe for all patients. You want a product that meets strict standards, such as FDA approval or CE marking. These certifications show that the gel is safe and works well in medical settings.
|
Criteria |
Importance |
|---|---|
|
FDA approval or CE marking |
Ensures safety and regulatory compliance for use in your region. |
|
Biocompatibility profile |
Confirms that the gel does not cause adverse tissue reactions or toxicity. |
|
Application process |
Evaluates how easy the gel is to apply, ensuring compatibility with surgical procedures. |
|
Evidence of efficacy |
Looks for clinical trial data or peer-reviewed studies demonstrating benefits. |
|
Cost implications |
Assesses whether the benefits justify the investment, considering potential reductions in complications. |
|
Contraindications or side effects |
Reviews safety profiles to avoid adverse outcomes. |
|
Integration with surgical protocols |
Ensures compatibility with existing workflows to streamline adoption. |
You should check the biocompatibility profile. This tells you if the gel will work well with human tissue. You also need to review any possible side effects. Always choose a gel that fits smoothly into your current surgical routines.
Effectiveness and Evidence
You want proof that the gel works before you use it. When Choosing the Right Anti Adhesion Gel for Your Hospital or Clinic, look for products with strong clinical evidence. Studies should show that the gel reduces adhesions and improves patient outcomes. For example, some studies compare gels made from hyaluronic acid with no treatment. These studies often measure how many patients develop adhesions, how severe the adhesions are, and how much pain patients feel after surgery.
|
Study Type |
Intervention |
Control |
Key Outcomes |
Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Comparative Study |
Auto-cross-linked hyaluronic acid gel |
No treatment |
Rate of adhesion formation, mean adhesion score, adhesion severity |
You want a gel that the body can break down safely. Biodegradability means the gel will not stay in the body longer than needed. It should turn into harmless byproducts that the body can absorb or remove. When Choosing the Right Anti Adhesion Gel for Your Hospital or Clinic, you need to match the gel's active period with the healing timeline of the tissue.
Application and Versatility
You want a gel that is easy to use in the operating room. The application method should fit your surgical workflow. When Choosing the Right Anti Adhesion Gel for Your Hospital or Clinic, look for products that spread well and stay where you put them. The gel should work with different tools and not slow down your team.
|
Application Method |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Connection |
The applicator should connect to the syringe with a Luer lock to avoid loosening. |
|
Positioning |
You can bend the rigid applicator and move it with forceps to reach the right spot. |
|
Application |
Use an intra-abdominal instrument to press the gel onto the tissue for a few minutes. |
You also want versatility. The best gels work in many types of surgeries, such as abdominal, pelvic, gynecological, and orthopedic procedures. These gels stick well to moist tissues and stay in place during surgery. They help reduce inflammation and support healing in different environments.
Gels adapt to many surgical sites.
They provide flexibility and stability.
Clinical evidence shows they are safe and effective for many procedures.
Manufacturer Reliability
You need to trust the company that makes your gel. When Choosing the Right Anti Adhesion Gel for Your Hospital or Clinic, check if the manufacturer has strong clinical trial data and meets all regulatory standards. Reliable companies invest in research and development. They keep up with new science and improve their products.
Clinical trial data proves the gel works and is safe.
Regulatory compliance means the gel meets all safety rules.
Vendor evaluation checks the company's history and ability to innovate.
Innovation shows the company can create better products as science advances.
Regulatory approvals, like FDA or CE marking, also matter. These approvals show that the manufacturer follows strict rules. They help you feel confident that the gel will work well in your hospital or clinic.
Tip: Choose innovative products for complex or minimally invasive procedures. Gels made from materials like hyaluronic acid or polylactic acid often perform well in these cases.
When you follow these steps for Choosing the Right Anti Adhesion Gel for Your Hospital or Clinic, you give your patients the best chance for a smooth recovery and fewer complications.
Practical Evaluation Tips
Product Evaluation Checklist
You can make better decisions by using a checklist when you compare anti-adhesion gels. A checklist helps you focus on what matters most for your hospital or clinic. Here is a table you can use to guide your evaluation:
|
Criteria |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Product Efficacy |
How well does the solution prevent adhesions? Look for clinical trial results and real-world data. |
|
Regulatory Approvals |
FDA, CE, or other certifications indicate safety and compliance. |
|
Technological Innovation |
Use of advanced materials or delivery methods can differentiate vendors. |
|
Ease of Use |
Compatibility with existing surgical procedures and ease of application matter. |
|
Cost-Effectiveness |
Balance between price and clinical benefits influences procurement decisions. |
|
Customer Support & Training |
Ongoing support ensures optimal product utilization. |
|
Global Reach & Distribution |
Availability across regions impacts scalability. |
|
Reputation & Clinical Adoption |
Peer-reviewed studies and surgeon testimonials validate effectiveness. |
Tip: Use this checklist during product trials or vendor meetings to keep your evaluation focused and objective.
Clinical Guidelines and Expert Input
You should always check the latest clinical guidelines before you choose a gel. Guidelines from trusted medical groups give you up-to-date advice on safe and effective products. You can also ask surgeons and clinical experts for their opinions. Their experience helps you understand how each gel works in real surgeries. Peer-reviewed studies and surgeon testimonials add another layer of confidence to your decision.
Review recommendations from surgical societies.
Ask for feedback from your surgical team.
Look for published studies and real-world results.
Cost and Supply Chain Factors
You need to think about cost and supply chain issues when you select an anti-adhesion gel. Changes in tariffs and input costs can affect how much you pay for these products. Some manufacturers now use local production to manage costs and keep products available. You must balance the price of the gel with its clinical benefits. Reliable supply chains help you avoid shortages and delays, which keeps your surgical schedule on track.
Note: Always check with your procurement team to make sure your choice fits your budget and supply needs.
Comparing Leading Gels
Feature Comparison
When you compare anti-adhesion gels, you want to focus on the features that matter most for your patients and your team. Each gel offers different strengths. You can use this list to guide your decision:
Effectiveness: Check how well the gel prevents adhesions in real surgeries.
Biocompatibility: Make sure the gel is safe, non-toxic, and does not cause inflammation.
Ease of Application: Look at how simple it is to use. Consider the gel's thickness and how you apply it during surgery.
Durability & Absorption: Find out how long the gel stays in place and how the body absorbs it after healing.
Regulatory Approval: See if the gel has approval from groups like the FDA or EMA. This shows it meets safety standards.
Cost & Reimbursement: Think about the price and if insurance covers it. This affects your hospital's budget.
Innovation & Differentiation: Some gels use new materials or special designs to work better.
Vendor Support & Training: Good companies offer training and support to help your team use the gel correctly.
When you choose an anti-adhesion gel, focus on these key points:
Safety and biocompatibility
Proven effectiveness
Biodegradability and proper duration
Easy application and versatility
Reliable manufacturer
A systematic, evidence-based approach helps you make the best choice for your patients. Use the checklist and comparison tools from this guide. You can feel confident in your decision and improve patient outcomes.
FAQ
What is the main purpose of anti-adhesion gel?
You use anti-adhesion gel to stop tissues from sticking together after surgery. This helps your patients heal faster and lowers the risk of pain or problems later.
How do you apply anti-adhesion gel during surgery?
You apply the gel directly to the area where you want to prevent adhesions. Most gels come with an applicator. You spread the gel evenly over the tissue before closing the surgical site.
Are anti-adhesion gels safe for all patients?
Most anti-adhesion gels are safe for many patients. You should always check for allergies or special conditions. Look for products with FDA or CE approval to ensure safety.
How long does anti-adhesion gel stay in the body?
The gel usually stays in the body for a few days to a few weeks. Your body breaks it down naturally. The exact time depends on the gel's material and your patient's healing process.
Can you use anti-adhesion gels in different types of surgeries?
Yes, you can use these gels in many surgeries. Surgeons use them in abdominal, pelvic, orthopedic, and gynecological procedures. Always check the product label for approved uses.